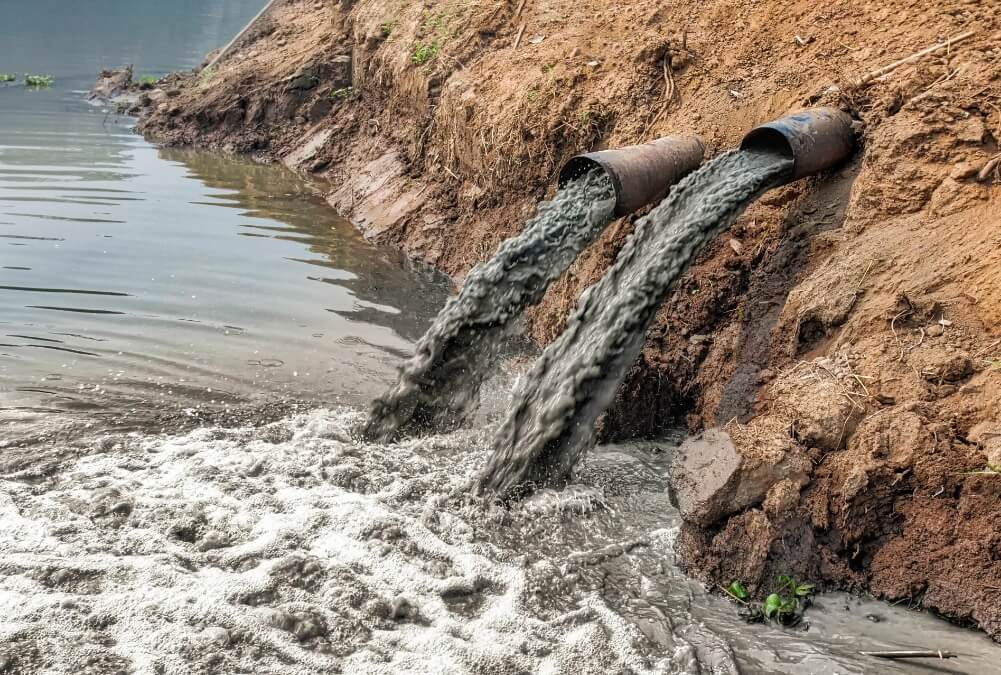



Water is at the core of sustainable development and is critical for socio-economic development, healthy ecosystems and for human survival itself. It is vital for reducing the global burden of disease and improving the health, welfare and productivity of populations.
An estimated 1.2 million people died as a result of unsafe water sources in 2017. This was 2.2% of global deaths.
Country-wise deaths from unsafe water sources
silverline
Billions More Can Now Drink 💧 Safely
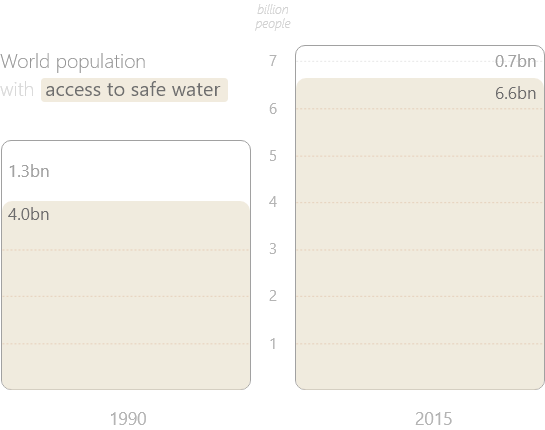
9/10 people now have access to drinkable water. It makes a HUGE difference to everything.
It massively decreases the risk of outbreaks of diarrhoea, cholera, dysentery, typhoid, polio and other major diseases.
Thirty years ago, only about 75% of the world had access to drinkable water. Today that number is at least 90% - thanks to concerted action from charities and governments.
Source: Our World Data, World Water
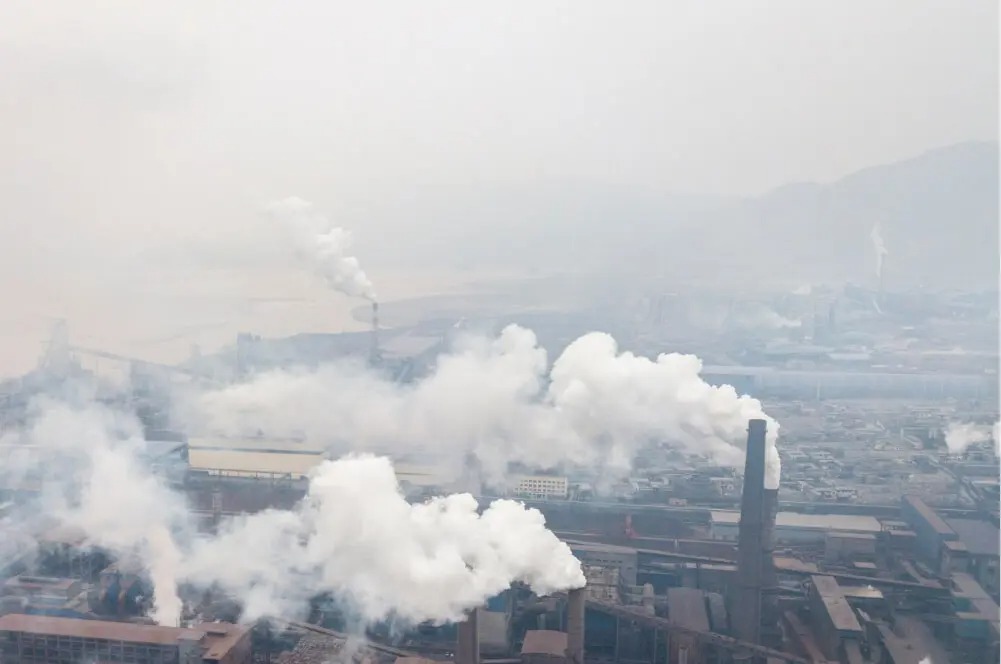


The World Health Organization (WHO) highlights air pollution as the number one reason for environment-related deaths. It’s estimated to be the cause of seven million premature deaths every year—4.3 million from indoor air pollution, and 3 million from ambient outdoor pollution.
Air pollution contributes to 9% of deaths globally – this varies from 2% to 15% by country
Air Pollution:London vs. Delhi
An estimated 6.5 million people die annually from air pollution
Air Pollution is a leading cause of many common killers:
7%
of lung cancer deaths
18%
of copd [Pulmonary disease deaths]
20%
of stroke deaths
34%
of heart disease deaths
An estimated 6.5 million people die annually from air pollution
silverline
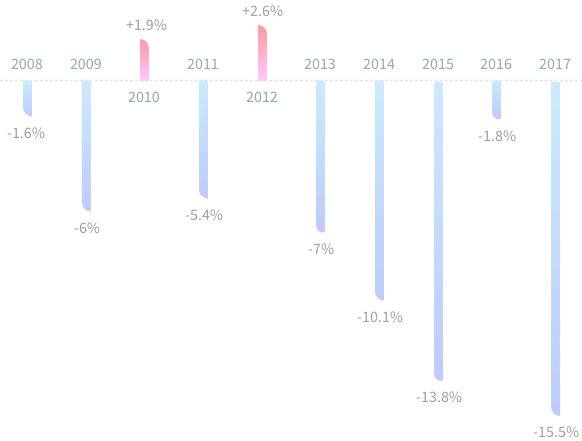
UK's Carbon Emissions 🏭 Are Falling Fast
Thanks to cleaner electricity and declining energy use
The UK is decarbonizing faster than any other high-income country.⠀
Less dependence on coal. Homes and factories using less electricity. Businesses cutting fuel consumption.
Source: mygridGB
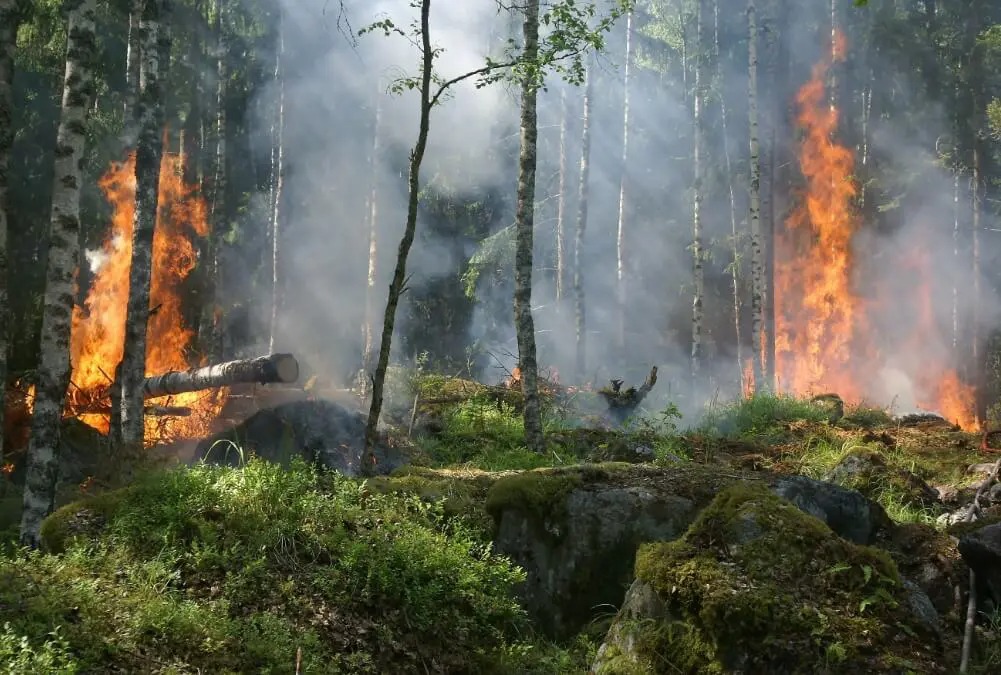


Wildfires occur when vegetated areas are set alight and are particularly common during hot and dry periods. They can occur in forests, grasslands, brush and deserts, and with sufficient wind can rapidly spread. The most common causes of fires are lightning strikes and man-made fires arising from deliberate arson or accidents.
In 2017, there were 71,499 wildfires compared to 65,575 wildfires in 2016. About 10 million acres were burned in 2017 compared with 5.4 million in 2016.
Source: National Interagency Fire Center
Country-wise Death Rate from Fires and Burns
half a billion (480 million) animals have been killed by the bush fires in Australia.
most common causes that led to the Australian bushfire:
1
climate change
2
indian ocean dipole
3
wind variability
4
lack of rainfall
Around 25,000 koalas were feared dead on Kangaroo Island

silverline
Forests 🌳🌳 owned by native people has risen 40%
It's a good thing because Deforestation-associated emissions are much lower on those lands, that means forests are in much safer hands.
Source: RightsandResources.org,
ForestLivelihoods.org



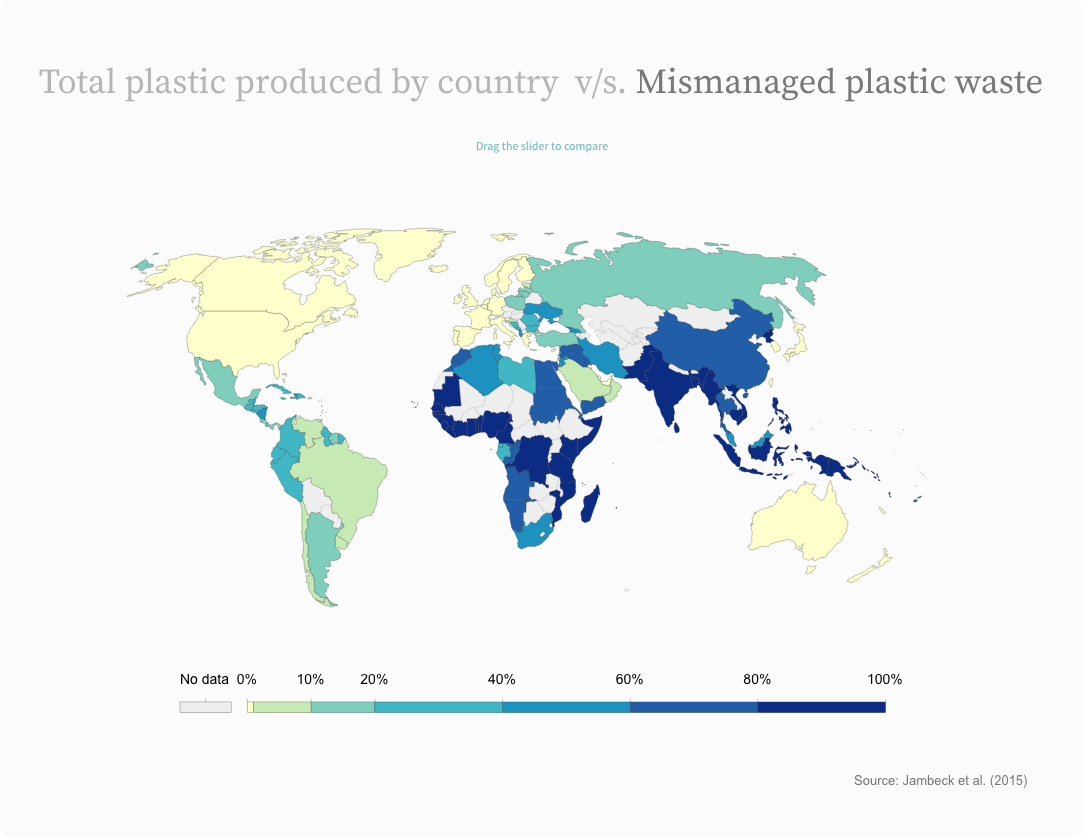
Plastic production has surged in the last 50 years, leading to widespread use of inexpensive disposable products that are having a devastating effect on the environment. Images of plastic debris-strewn beaches and dead animals with stomachs full of plastic have sparked outrage.
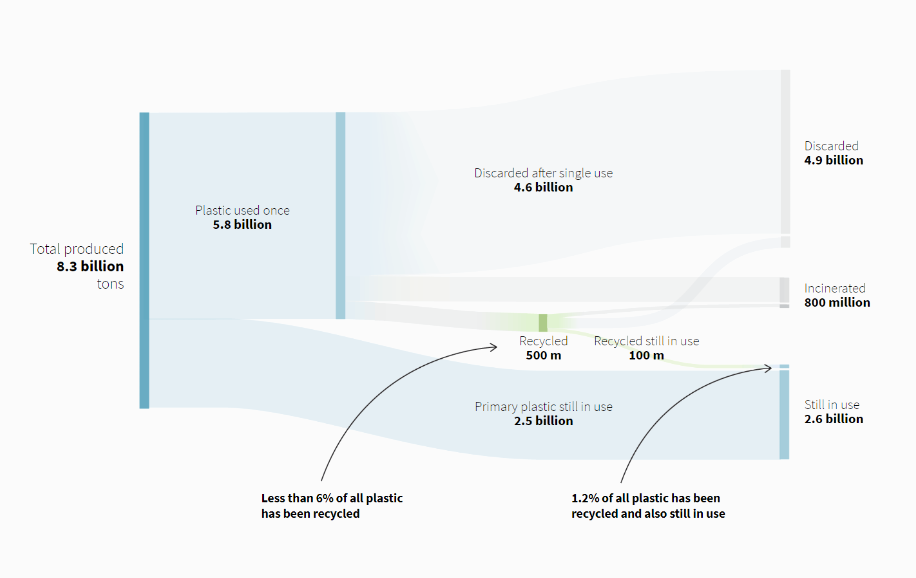
World had produced 7.8 billion tonnes of plastic i.e more than one tonne of plastic for every person alive today.
And guess what!
A whopping 91% of plastic isn't recycled.
World's addiction to Plastic
Every minute 1,000,000 plastic bottles are sold.
Total plastic produced by country v/s. Mismanaged plastic waste
Drag the slider to compare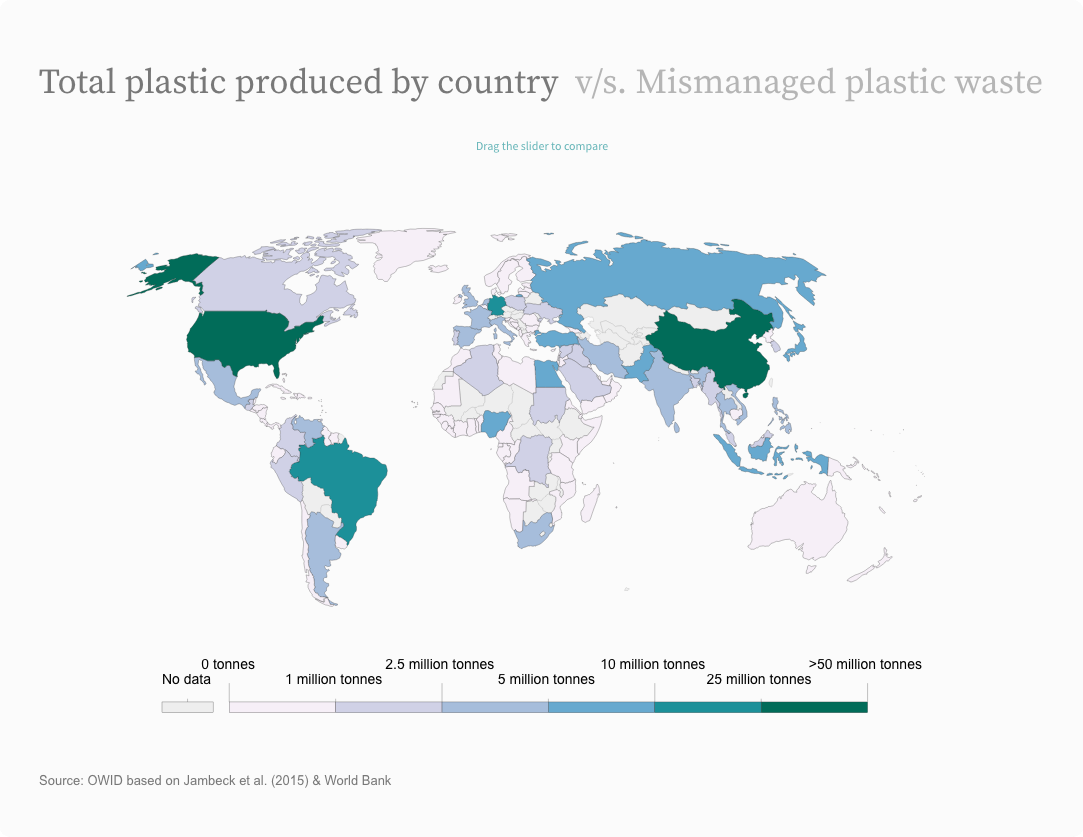

silverline
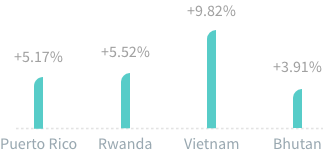
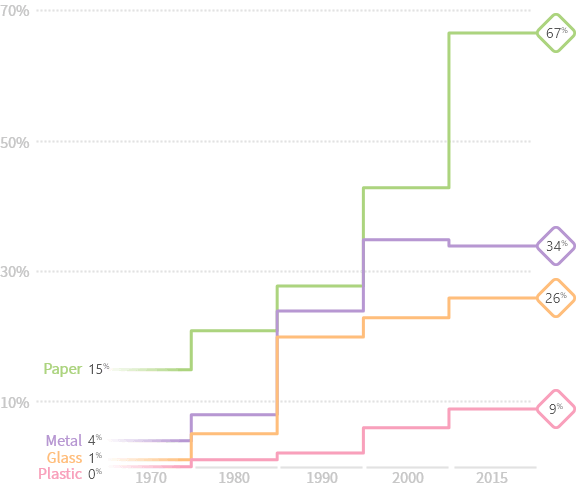
US recycling rates ♻️ are finally picking up
Thanks to each states individual responsibility
There is no national law in the United States that mandates recycling, and state and local governments often introduce their own recycling requirements.
Some cities, such as Seattle, and states like Connecticut, have created mandatory recycling laws that may fine citizens who throw away a certain percentage of recyclable materials in their garbage waste.
Source: US Environmental Protection Agency
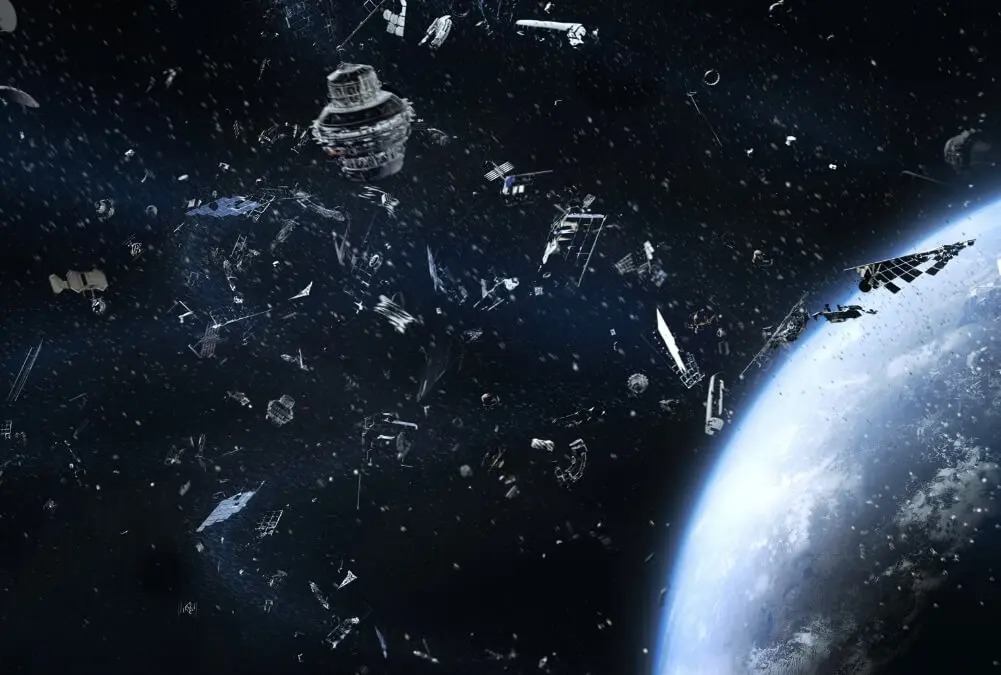


Space debris has become a huge problem. Hundreds of thousands of man-made objects are zipping around our planet—from dead satellites to errant nuts and bolts, putting our working satellites at risk.
Junk accumulation in Earth’s orbit has become a hindrance and can endanger future missions to the moon or Mars.
The US government logged 308,984 potential space-junk collisions in 2017 - and the problem could get much worse.
Countries with the most spacejunk & what it is
Average speed of debris 22,369 MPH
Orbital debris orbiting around the earth:
8000
KG of man made stuff
14000 +
old rocket parts
4600+
satellites
95%
space junk out of control
Probability of a working satellite being hit by debris is 3% in 5-10 years
silverline
Policies in Pipeline, to remove debris
The European Space Agency (ESA) is part of an international effort to monitor and – ultimately – tackle space debris. This junk – accumulated in orbit since the dawn of the space age sixty years ago – poses an increasing risk to operational spacecraft
ESA is developing missions to tackle the problem to help prevent a serious collision in space. The Agency is also monitoring possible dangers caused by fragments of redundant spacecraft falling to Earth, such as China’s space station Tiangong-1 – due to enter the atmosphere in the coming months.
Source: www.esa.int
