A Gantt chart visualization shows activities (tasks or events) displayed against time, most commonly used for the purpose of project management and scheduling. On one axis is a list of the activities and along the other is a suitable time scale. Each activity is represented by a bar; where the position and length of the bar reflect the start date, duration, and end date of the activity. Gantt charts are usually created initially using an early start time approach, where each task is scheduled to start immediately when its prerequisites are complete. This method maximizes the float time available for all tasks.
[chartdesc]
History of Gantt Chart
Revolutionary when introduced, the first Gantt chart was known as a harmonogram devised in the mid-1890s by Karol Adamiecki, a Polish engineer. Some 15 years after Adamiecki, Henry Gantt, an American engineer and project management consultant, devised his own version of the chart and it became widely known and popular in the Western countries.
These kinds of data visualization charts were handmade earlier, any changes in the project required redrawing the entire charts simultaneously. However, with the advent of computers, the process became significantly easier. And by 2012, almost all Gantt charts were made by software that can easily adjust to schedule changes.
[chartimg]
When to Use a Gantt Chart?
1To complete a time-based planning for activities and scheduling
Use Gantt charts to create and track project schedules by listing the various activities and creating timelines for each activity. Gantt charts are useful for setting milestones based on timelines, as they allow one to mark important dates one needs to be aware of. The information on how the tasks relate to each other, how far each task has progressed, and what resources are being used for each task are captured to ensure a smooth tracking of project schedules and managing project activity.
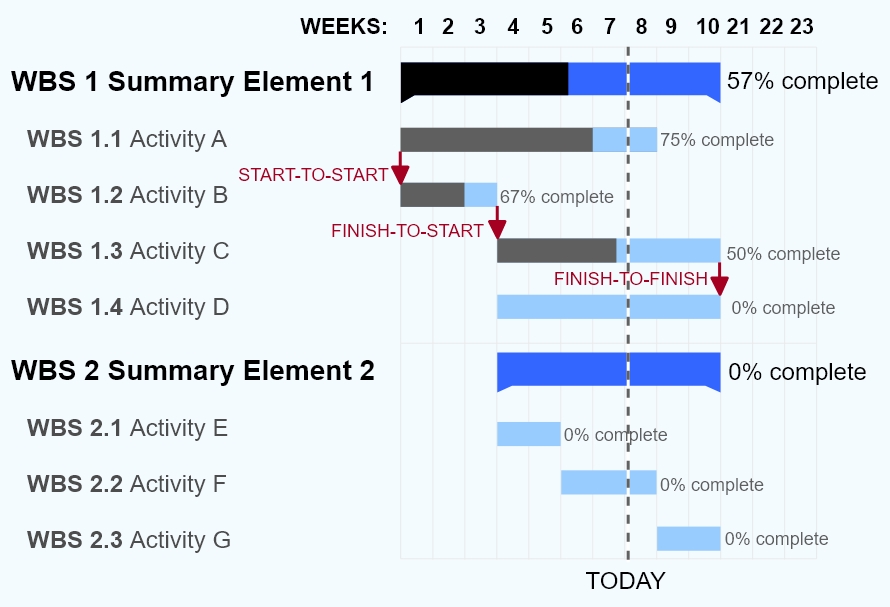
2For understanding interdependencies and how activities overlap with others
Gantt chart software typically provides mechanisms to link task dependencies, although this data may or may not be visually represented. Gantt charts and network diagrams are often used for the same project, to show which tasks are linked together. Links are shown with lines on the Gantt chart, and the arrow points to the task that comes next. Use a Gantt chart visualization to set up dependencies as start-to-finish, start-to-start, finish-to-finish, or finish-to-start and allocate capacity as required.
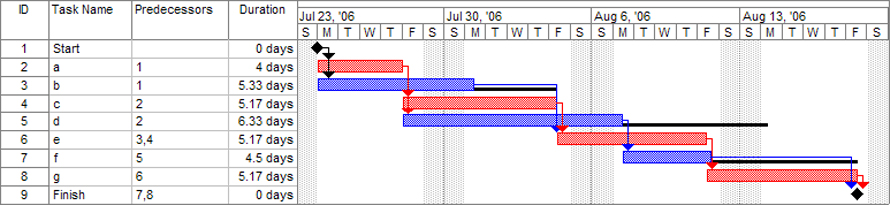
3When required to determine planned vs actual progress
Gantt charts can be useful to measure and indicate progress. This can be represented in a couple of different ways on the Gantt chart. Shading on the activity bar can indicate how complete the planned work is and when the bar is totally shaded, the representation indicates that the task is finished. One can also see a view of the actual progress versus the planned progress using color differentiation.
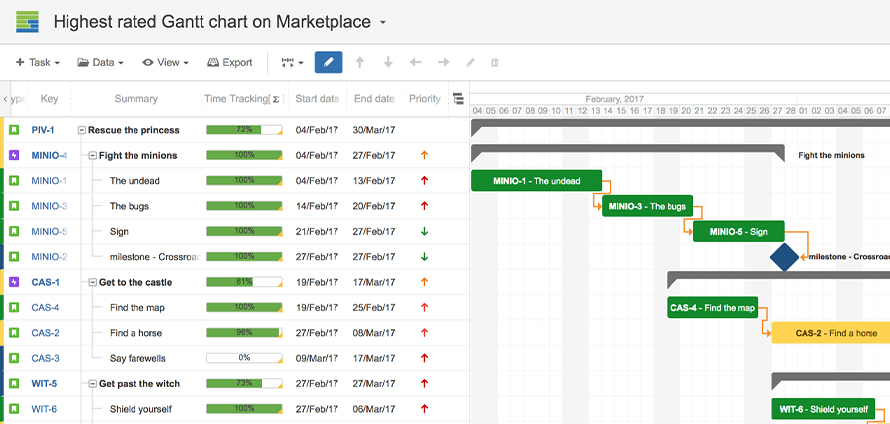
Types of Gantt Chart
1. Progress Gantt chart
Here tasks are shaded in proportion to the degree of their completion. A vertical line is drawn at the time index when the progress Gantt chart is created, and this line can then be compared with shaded tasks. If everything is on schedule, all task portions left of the line will be shaded, and all task portions right of the line will not be shaded. This provides a visual representation of how the project and its tasks are ahead or behind schedule.
2. Linked Gantt charts
These contain lines indicating the dependencies between tasks. However, a linked Gantt chart visualization can quickly become cluttered in all but the simplest cases. Critical path network diagrams are superior to visually communicate the relationships between tasks.
When Not to Use a Gantt Chart?
1When one needs a regular update of the chart
Gantt charts can be tedious to update on paper and can become unmanageable for a detailed project plan. It relies upon the work breakdown structure to have already been constructed – and for it to be complete. If a major milestone is missing, the Gantt chart will not indicate that and one might need to recreate the entire project schedule if something is left out, a duration if misestimated.
However, using online tools may drastically simplify the process. For instance, a ready-to-use Tableau Gantt chart data structure will help you instantly set it up.
2When the project is complex in nature
Gantt chart only works well with smaller projects and once the durations and tasks stretch past one page, the Gantt chart begins to lose its functionality. This makes the chart difficult to view on a computer screen and too complex to depict if the tasks contain sub-tasks for representation.
3When costs and scope also need to be represented
Gantt charts do not do well with dealing with project triple constraints of time, cost, and scope. The cost of a project is not depicted on a Gantt chart. Also, the full scope of a project cannot be depicted in a Gantt chart. No matter how detailed the Gantt chart is, the full complexity is not depicted. This is because the main focus of the Gantt chart is time.