Technology is evolving unprecedentedly, and mixed reality (MR) is at the forefront of this transformation. By merging the physical world that we exist in with digital content that’s incessantly consumed, MR offers immersive experiences that redefine how we interact with technology globally.
“I feel that Augmented reality is perhaps the ultimate computer.”
— Satya Nadella | CEO, Microsoft
But what exactly makes mixed reality design the next frontier in product design? How does it enable users to experience immersive interactions that bridge the real-world experience and 3D world? Let’s dive in.
Stuti Mazumdar & Vidhi Tiwari - August 2024

Understanding Mixed Reality: Where AR and VR Converge
To fully appreciate the potential of mixed reality applications, it’s essential to understand how MR differs from both augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely virtual environment to block out the real world, or Augmented Reality (AR), which overlays digital elements (text, images, or 3D models) onto the surroundings of the user, mixed reality seamlessly integrates real and virtual elements, allowing them to coexist and interact dynamically. Take the example of Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap, or devices. Mixed-reality design creates seamless, immersive experiences where virtual objects feel as natural and interactive as physical ones.
You can witness this magic across various digital experiences ranging from gaming and entertainment to education, healthcare, and enterprise applications—mixed reality applications are expanding rapidly, transforming industries and enhancing user experiences
Key UX Considerations for Mixed Reality:
1. Field of View (FoV)
Unlike traditional screens, MR requires an adaptive field of view to ensure that the virtual objects overlaying the interface remain visible and intuitive to interact with at all times for the user, regardless of their absolute position across the experience.
2. 3D Space Awareness
MR interfaces inherently exist in a 3D space, meaning that designers must consider the overall depth and spatial positioning of all the real-world interactions they mimic in the “digital” environment.
3. Gesture & Voice Commands
With MR devices like HoloLens and Magic Leap, users interact through hand gestures, voice commands, and eye movements instead of traditional touchscreens. Ensuring the experience is sensitive to these gestures to the right degree while allowing them to explore the environment freely is critical.
4. User Comfort
Avoiding motion sickness, ensuring easy navigation, and designing for diverse users remain priorities in mixed reality design. Following accessibility guidelines in these circumstances is paramount.
Designing for Mixed Reality: Challenges & Opportunities
While mixed reality design unlocks incredible possibilities, it also presents challenges:
1. Technical Limitations
MR headsets still face limitations like battery life, processing power, and field of view. While we’re witnessing continuous efforts to improve the supporting hardware of these experiences, designers must optimize experiences to ensure smooth performance.
2. User Adaptation
MR, unlike traditional user interfaces, relies on voice commands, gestures, and 3D interactions, which require new interaction models. Clear onboarding and intuitive design are crucial to enable users to effortlessly use this new tech.
3. Blending the Digital with Our Reality
Ensuring that virtual objects feel natural within the physical world is key to creating immersive and realistic experiences.
Despite these challenges, MR offers endless opportunities for innovation, engagement, and transformation across industries.
Real-World Applications of Mixed Reality
MR is no longer confined to sci-fi movies—it is actively transforming industries. Let’s go through a few examples of successful MR digital experiences across industries:
Gaming & Entertainment

MR is redefining gaming by enabling real and virtual worlds to interact in real-time. Gamers can move around their actual environment while engaging with virtual objects, creating highly immersive experiences.
Microsoft’s HoloLens enables users to play interactive games in their living rooms, where digital characters interact with real surfaces “around them”.
Healthcare & Medical Sciences

Doctors and medical students are using mixed reality applications to practice complex procedures in a virtual environment while remaining connected to the real world to ensure smarter medical practices.
Surgeons use 3D space visualizations of human anatomy to perform precision-based surgeries with enhanced accuracy.
Architecture & Interior Design
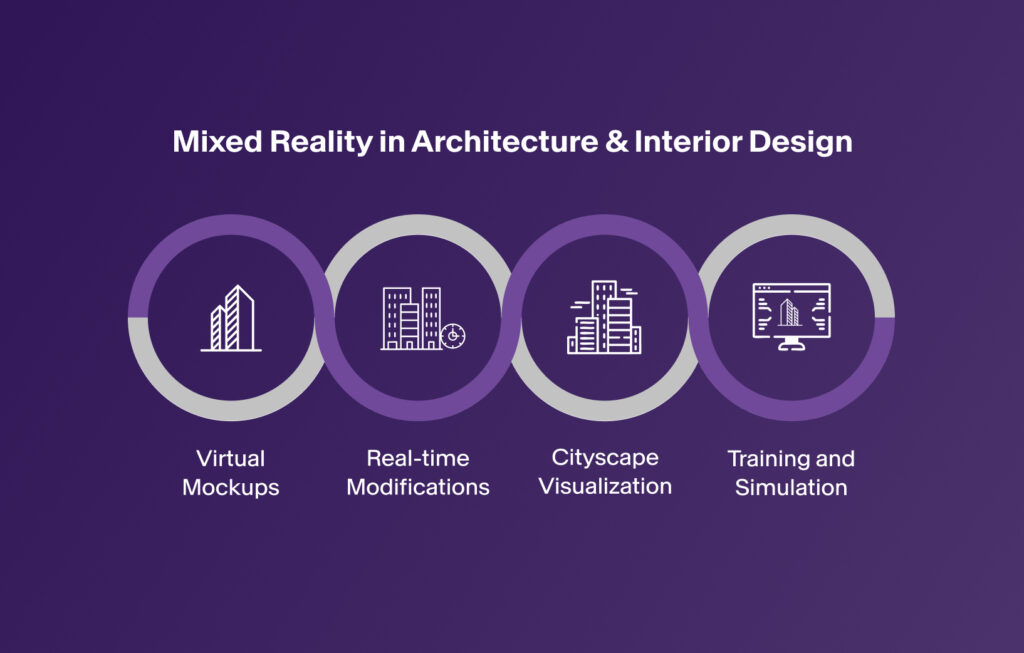
MR allows architects and designers to visualize projects in real-world environments before their construction projects even begin. Clients can walk through virtual spaces and make real-time adjustments to ensure maximum safety and accessibility of the construction project.
Education & EdTech
As technology advances, MR will become more accessible, lightweight, and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives. We can already envision a few advancements: AI-powered MR experiences will enable devices to predict user needs, making interactions even more intuitive; MR glasses and wearables will replace bulky headsets, making wearable tech mainstream; voice commands and natural interfaces will make MR interactions smoother and more human-like. The convergence of AI, 5G, and spatial computing will drive mixed reality applications to new heights, revolutionizing how we experience the physical world and digital content.
Mixed reality is not just the future—it’s happening now. By integrating real and virtual elements, MR is redefining how we engage with technology, offering immersive experiences that feel intuitive and transformative.